FLATULENCE : Causes, Symptoms and More
It is gas formation in stomach and intestine.
- High fiber diet – beans, vegetables, fruits and grains.
- Partially digested food on which bacteria can grow and produce gas.
- Constipation.
- Ingestion of air in the digestive tract while eating / drinking – when eating too quickly, while drinking through straw, smoking, and while eating chewing gums.
- Infection of digestive tract may increase the gas production.
- Obesity.

SIGN AND SYMPTOMS:
- Bloating of abdomen.
- Pain in abdomen.
- Audible passage of air – as belching from mouth or as flatus from rectum.
- Gas can be offensive.
DIETARY MANAGEMENT:
- Go for a walk after meals, but not do brisk walking.
- Eat slowly and chew food properly.
- If gas is offensive, limit intake of proteins like- meat, eggs.
- Limit intake of high carbohydrates – rice, potatoes, sweet potatoes etc.
- Avoid pulses and fibrous vegetables like cabbage and cauliflower.
- Avoid cheese, beans, alcohol, soy sauce, carbonated drinks – coke etc.
- Avoid fried and spicy food.
- Add little garlic and asafetida in your diet – helps in digestion and prevents gas formation.
- Take plenty of fluids.
- Avoid over eating, frequent small meals are advisable.
- Curd and butter milk may help to change the intestinal flora.
- If over weight reduce weight.
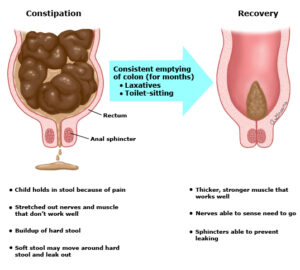
CONSTIPATION
Difficulty in passing stool or passes once in 2 / 3 days, stools can be hard or soft is termed as constipation. Even ineffectual urge or a sensation of incomplete stools can be termed as constipation.

CAUSES:
- Modern life style – not eating enough and drinking little water, lack of exercise.
- Emotional or psychological problems.
- Sedentary life.
- Eating too much of meat and dairy products.
- Chronic abuse of laxatives.
- Bottle fed babies.
- Pregnancy.
- Certain drugs like antacids, iron, calcium, blood pressure medications.
- Certain digestive tract diseases.
- School going children are shy to tell teacher, and later develops a habit to ignore the urge.
- Cooking in aluminum, iron vessels.
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS:
- Stools every 2nd or 3rd day.
- Difficulty in expelling feces from rectum.
- Painful evacuation of feces.
- Pain sometimes remains for hours after passing stool.
- Hard stools.
- Occasional blood in stool due to fissure, fistula or piles.
DIETARY MANAGEMENT:
- Drink at least 2-3 liters of water a day.
- Eat high fiber diet – whole grains, bran, oat, green leafy vegetables, peas, beans, potatoes, raw vegetables, salads, dried fruits and fresh fruits.
- Eat fruits and vegetables with the skin.
- Avoid food that can cause constipation like pomegranate etc.
- You can take one spoon isabgul (fiber, Psyllium) in water before retiring to bed.
- Walk after every meals.
- Drink 2- 4 glasses of warm water every morning.
- Limit intake of laxatives.
NOTE
- Do not suppress the urge to pass stools.
- Get a regular time fixed to the toilet.